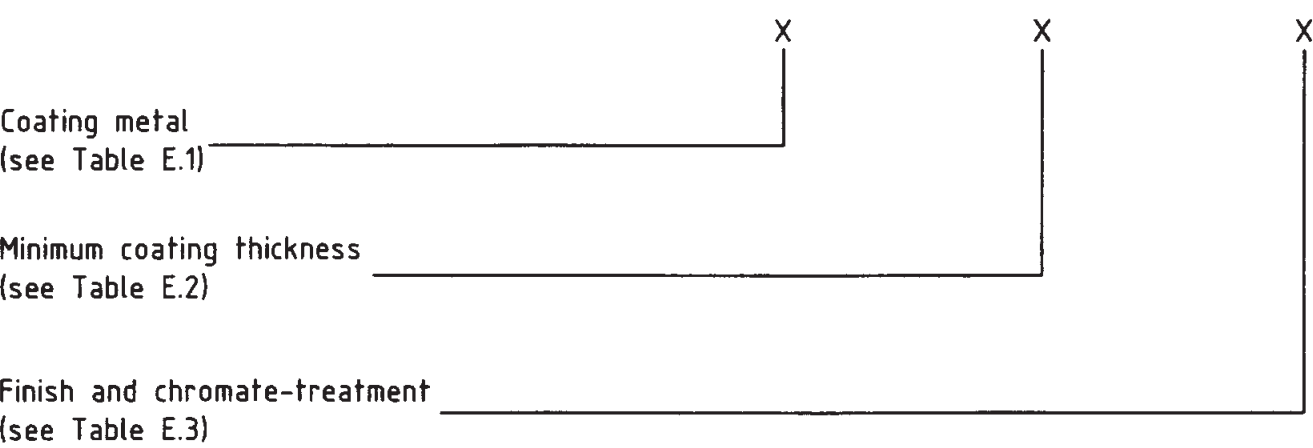
ISO 4042 Specification
- Code system A
- Coating metal/alloy
- Coating thickness(total deposit thickness)
- Finish and chromate treatment
- Designation
- Examples for coating designation Electroplated zinc conting, coating thickness 8 µm, bright, with yellow iridescent chromate conversion coating.
- Reagents
- Calculations
- Examples for coating designation Electroplated nickel coating, thickness 20 µm, bright, plus regular coating of chromium (0,3 µm).
| Coating metal/alloy | Designation | |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Elements | |
| Zn | Zinc | A |
| Cda | Cadmium | B |
| Cu | Copper | C |
| CuZn | Brass | D |
| Ni b | Nickel | E |
| Ni b Cr rb | Nickel-chromium | F |
| CuNi bb | Copper-nickel | G |
| CuNi b Cr rb | Copper-nickel-chromiumc | H |
| Sn | Tin | J |
| CuSn | Copper-tin(bronze) | K |
| Ag | Silver | L |
| CuAg | Copper-silver | N |
| ZnNi | Zinc-nickel | P |
| ZnCo | Zinc-cobalt | Q |
| ZnFe | Zinc-iron | R |
| a Use of cadmium is restricted
or prohibited in
certain
countries. b For ISO classification code see ISO 1456. c Thickness of chromium approximately 0,3 µm. |
||
| Coating thickness, μm | Designation | |
|---|---|---|
| one coating metal | two coating metalsa | |
| no coating thickness required | -- | 0 |
| 5 | 2+3 | 2 |
| 8 | 3+5 | 3 |
| 10 | 4+6 | 9 |
| 12 | 4+8 | 4 |
| 15 | 5+10 | 5 |
| 20 | 8+12 | 6 |
| 25 | 10+15 | 7 |
| 30 | 12+18 | 8 |
| a The thicknesses specified for the first and the second coating metal apply for all coating combinations except that chromium is the top coating which has always a thickness of 0.3 µm. | ||
| Finish | Passivation by chromate treatment a: typical colour | Designation |
|---|---|---|
| Dull | no colour | A |
| bluish to bluish iridescent b | B | |
| yellowish gleaming to yellow-brown, iridescent | C | |
| drab olive to olive brown | D | |
| Semi-bright | no colour | E |
| bluish to bluish iridescent b | F | |
| yellowish gleaming to yellow-brown, iridescent | G | |
| drab olive to olive brown | H | |
| Bright | no colour | J |
| bluish to bluish iridescent b | K | |
| yellowish gleaming to yellow-brown, iridescent | L | |
| drab olive to olive brown | M | |
| High-bright | no colour | N |
| Optional | like B,C or D | P |
| Dull | brown-black to black | R |
| Semi-bright | brown-black to black | S |
| Bright | brown-black to black | T |
| All finishes | no chromate treatment c | U |
|
a Passivation treatments are possible only with zinc or
cadmium coatings. b Applies to zinc coating only. c Example for such a coating: A5U |
||
Example:
A hexagon head to 150 4014 M10×60 88 with electroplated zinc coating (A from Table
) having a minimum coating Bickness of 5 µm (2 from Table)
and brightness
condition "bright" being chromated yellow iridescent (from Table) is designated
as follows:
Hexagon head bolt ISO 4014 - M10×60-8.8-A2L
NOTE 1: If по minimum coating thickness is explicitly required, then the symbol "0"
of
the coating thickness according to Table 2 should the indicated in the code number
for example ADP so that the code number contains complete specifications symbol "0"
apptes comesporidingly to threaded parts below M1,6 or other very small parts.
NOTE 2: If other treatments are required, for example greased or oiled, this should
be
agreed upon.If applicable, this treatment may be added to the designation as clear
text.
| Designation to system A:A3L | Designation to system B:Fe/Zn8c2C |
|---|---|
| where | where |
| -- A refers to Zn | -- Fe refers to the basic metal |
| -- 3 is the code number for 8 μm | -- Zn refers to the coating metal |
| -- L refers to bright with yellow iridescent chromate conversion coating | -- 8 is the minimum coating thickness in μm |
| -- c refers to chromate conversion coating. | |
| -- 2 is the class of chromate conversion coating. | |
| -- C is the type of chromate conversion coating. |
The stripping solutions consist of one of the following:
a) Stripping solution A
--- antimony trioxide: 120 g/l
--- hydrochloric acid (p > 1.16 g/ml) to make up to a one litre solution
b) Stripping solution B
--- sodium meta-nitrobenzene sulfonate: 65 g
--- sodium hydroxide: 10 g
--- sodium cyanide: 100 g
Make up to a one litre solution with water
c) Stripping solution C
--- orthophosphoric acid (p = 1.75 g/ml)
NOTE: It is dangerous for water to come into contact with the hot acid; water
lost
by
evaporation should be replaced only wa the solution has cooled.
Proprietary chemical stripping solutions for nickel may be used provided it can
be
shown
that there is only neglig attack on the base metal (ie. less than 0,5 µm of base
metal
being removed).
Calculate the batch average thickness of coating, in micrometres, using the
following
formula:
Batch average thickness = K x (m0 - m1)/A
where
K = 10000/p = 1120, assuming the mass density of nickel p = 8.9g/cm3;
m0 is the original mass, in grams, of the sample;
m1 is the final mass, in grams, of the sample;
A is the total area, in square centimetres, of the parts of the sample.
The surface area A can be evaluated according to informative annex G.
| Designation to system A. F6J | Designation to systern B: Fe/Ni 20b Cr r |
|---|---|
| where | where |
| -- F refers to nickel-chromium with chromium 0.3 µm | -- Fe refers to the basic metal |
| 6 is the code number for 20 µm | Ni refers to the coating metal |
| J refers to bright, no colour | 20 is the minimum coating thickness of nickel in µm |
| b refers to bright | |
| Cr refers to the chromium coating | |
| r refers to regular (i.e.0.3 µm) |
